1. 학부 연구생 민상
- 난이도
- 골드 5
- 시간 제한
- 1초
- 메모리 제한
- 512MB
- 출처
A. 📜 문제
위 백준 사이트에 접속하여 문제를 확인해주세요.
B. 💡 내 답안
a. 😅 1차 시도 (실패)
def dfs(graph, visited, x, y, d):
global n, m
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < m:
if d[0] == 0 and d[1] == 0:
pass
else:
if graph[x][y] != 9:
visited[x][y] = True
dd = d[:]
if graph[x][y] == 1:
if dd[1] == 1 or dd[1] == -1:
dd = (0, 0)
elif dd[0] == 1 or dd[0] == -1:
pass
elif graph[x][y] == 2:
if dd[0] == 1 or dd[0] == -1:
dd = (0, 0)
elif dd[1] == 1 or dd[1] == -1:
pass
elif graph[x][y] == 3:
# 빨간선
if dd[0] == 1 and dd[1] == 0:
dd = (0, -1)
# 초록선
elif dd[0] == 0 and dd[1] == -1:
dd = (1, 0)
# 보라선
elif dd[0] == -1 and dd[1] == 0:
dd = (0, 1)
# 파란선
elif dd[0] == 0 and dd[1] == 1:
dd = (-1, 0)
elif graph[x][y] == 4:
# 빨간선
if dd[0] == 0 and dd[1] == -1:
dd = (-1, 0)
# 초록선
elif dd[0] == -1 and dd[1] == 0:
dd = (0, -1)
# 보라선
elif dd[0] == 0 and dd[1] == 1:
dd = (1, 0)
# 파란선
elif dd[0] == 1 and dd[1] == 0:
dd = (0, 1)
dx = x + dd[0]
dy = y + dd[1]
dfs(graph, visited, dx, dy, dd)
return
def check_place(graph, air_conditioners):
global n, m
ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
for x, y in air_conditioners:
visited[x][y] = True
for d in ds:
dx = x + d[0]
dy = y + d[1]
dfs(graph, visited, dx, dy, d)
place_count = count_visit(visited)
return place_count
def count_visit(visited):
global n, m
count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if visited[i][j]:
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = []
air_conditioners = []
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
for j in range(m):
if temp[j] == 9:
air_conditioners.append((i, j))
# print(*graph, sep='\n')
# print(air_conditioner)
print(check_place(graph, air_conditioners))
b. 😊 2차 시도 (성공)
def bfs(graph, visited, x, y, d):
global n, m
while True:
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < m:
if d[0] == 0 and d[1] == 0:
break
else:
if graph[x][y] != 9:
visited[x][y] = True
if graph[x][y] == 1:
if d[1] == 1 or d[1] == -1:
d = (0, 0)
elif d[0] == 1 or d[0] == -1:
pass
elif graph[x][y] == 2:
if d[0] == 1 or d[0] == -1:
d = (0, 0)
elif d[1] == 1 or d[1] == -1:
pass
elif graph[x][y] == 3:
# 빨간선
if d[0] == 1 and d[1] == 0:
d = (0, -1)
# 초록선
elif d[0] == 0 and d[1] == -1:
d = (1, 0)
# 보라선
elif d[0] == -1 and d[1] == 0:
d = (0, 1)
# 파란선
elif d[0] == 0 and d[1] == 1:
d = (-1, 0)
elif graph[x][y] == 4:
# 빨간선
if d[0] == 0 and d[1] == -1:
d = (-1, 0)
# 초록선
elif d[0] == -1 and d[1] == 0:
d = (0, -1)
# 보라선
elif d[0] == 0 and d[1] == 1:
d = (1, 0)
# 파란선
elif d[0] == 1 and d[1] == 0:
d = (0, 1)
x = x + d[0]
y = y + d[1]
else:
break
else:
break
return
def check_place(graph, air_conditioners):
global n, m
ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
for x, y in air_conditioners:
visited[x][y] = True
for d in ds:
dx = x + d[0]
dy = y + d[1]
bfs(graph, visited, dx, dy, d)
place_count = count_visit(visited)
return place_count
def count_visit(visited):
global n, m
count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if visited[i][j]:
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = []
air_conditioners = []
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
for j in range(m):
if temp[j] == 9:
air_conditioners.append((i, j))
# print(*graph, sep='\n')
# print(air_conditioner)
print(check_place(graph, air_conditioners))
c. 😊 3차 시도 (성공)
def wind_move(graph, visited, x, y):
"""
바람이 지나가는 자리를 구함.
:param graph:
:param visited: 방문한 위치 (mutable 객체라 따로 return하지 않음)
:param x: 에어컨 x좌표
:param y: 에어컨 y좌표
:return:
"""
global n, m
ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
# 이 부분은 블로그에 그림으로 설명할 예정
item = {1:(9, 1, 9, 3),
2:(0, 9, 2, 9),
3:(3, 2, 1, 0),
4:(1, 0, 3, 2)}
for i in range(4):
d = ds[i]
dx = x + d[0]
dy = y + d[1]
while True:
# 연구실을 벗어나는 경우
if 0 <= dx < n and 0 <= dy < m:
# 현재 위치가 에어컨이 아닌 경우
if graph[dx][dy] != 9:
visited[dx][dy] = True
# 현재 위치에 물건이 있는 경우
if graph[dx][dy] in (1, 2, 3, 4):
i = item[graph[dx][dy]][i]
# 물건1, 물건2로 인해 더 이상 이동하지 못하는 경우
if i == 9:
break
else:
d = ds[i]
dx += d[0]
dy += d[1]
else:
break
else:
break
return
def check_place(graph, air_conditioners) -> int:
"""
에어컨별로 바람의 경로를 구함.
:param graph:
:param air_conditioners:
:return: 바람이 지나가는 자리의 수
"""
global n, m
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
for x, y in air_conditioners:
visited[x][y] = True
wind_move(graph, visited, x, y)
return count_visit(visited)
def count_visit(visited) -> int:
"""
바람이 지나가는 자리의 갯수를 구함
:param visited: 바람이 지나가면 true
:return: 바람이 지나가는 자리의 수
"""
global n, m
count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if visited[i][j]:
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = []
air_conditioners = []
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
for j in range(m):
if temp[j] == 9:
air_conditioners.append((i, j))
# print(*graph, sep='\n')
# print(air_conditioner)
print(check_place(graph, air_conditioners))
a. 🙄 회고
내 풀이
- 이런 종류의 문제는 dfs로 푼 기억이 있어서 dfs로 접근했다.
반성
- 조건이 최대 연구실의 크기가 2000 * 2000까지 라고 적혀있었지만, 설마 2000까지 탐색하겠어? 라는 안일한 생각으로 접근했다.
C. 🧐 문제 해설
이해한 내용을 바탕으로 작성했습니다.
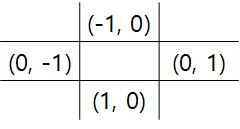
바람은 위 그림처럼 4방향으로 이동할 수 있다.
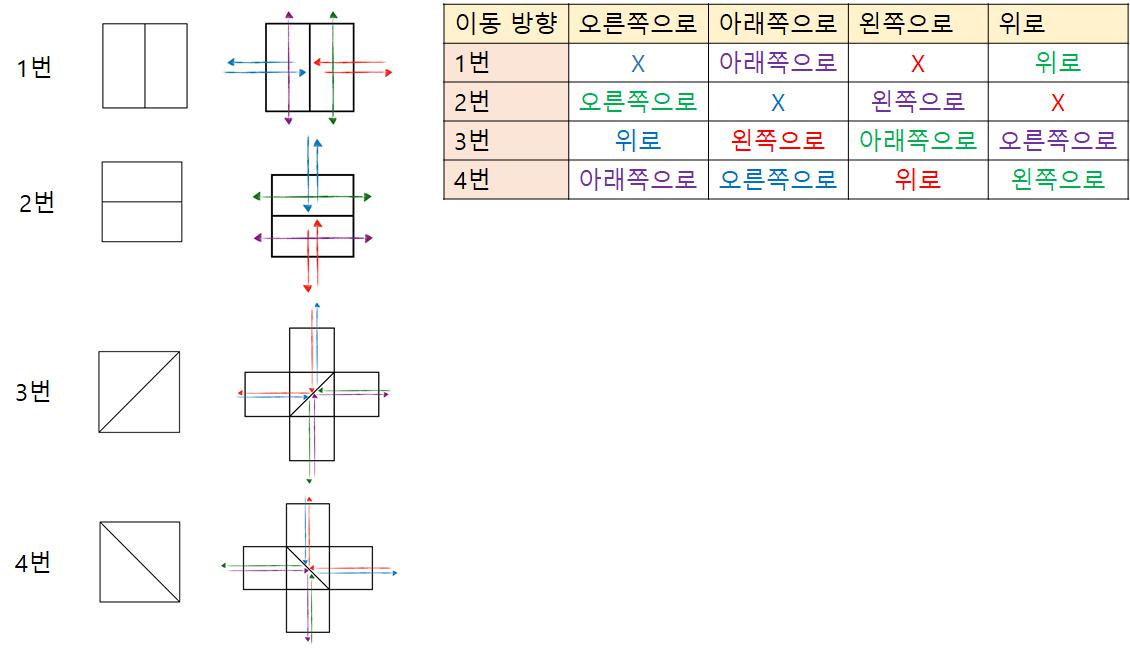
바람이 물건을 만나면 방향이 위 표와 같이 바뀐다.
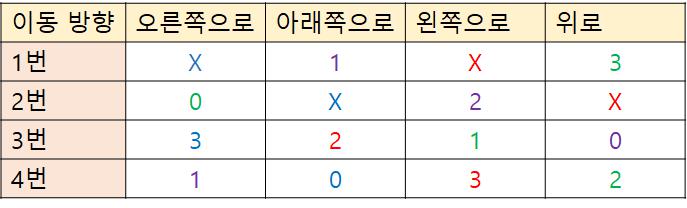
바람의 방향을 오른쪽, 아래쪽, 왼쪽, 위쪽 순서로 생각하면, (0, 1, 2, 3) 인덱스가 할당된다.
그럼 위와 같이 바람이 물건을 만났을 때 변경될 인덱스를 구할 수 있다.
위 부분을 알면 이 문제는 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
바람이 방문한 지점을 따로 체크하고, 조건에 맞춰 자리에 바람이 오는지를 확인하면 된다.
바람이 사라지는 경우는 1. 맵을 벗어나거나, 2. 1번, 2번 물건을 만나거나 3. 에어컨을 만나는 경우이다.
참고문헌
baekjoon. 21922번: 학부 연구생 민상 (acmicpc.net). Baekjoon. (accessed Dec 23, 2021)