1. 블록 이동하기
- 난이도
- 상
- 풀이 시간
- 50분
- 시간 제한
- 1초
- 메모리 제한
- 128MB
- 출처
A. 문제
위 프로그래머스 사이트에 접속하여 문제를 확인해주세요.
B. 내 답안
a. 1차 시도 (실패)
from collections import deque
def solution(board):
check_move_board = [i[:] for i in board]
q = deque()
q.append([0, 0, 0, 1])
q.append([0, 1, 0, 0])
q_set = set()
q_set.add((0, 0))
q_set.add((0, 1))
time = 0
cir_ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
move_ds = ((0, 1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 1, 0), (0, -1, 0, -1), (-1, 0, -1, 0))
n = len(board)
while q:
a_x, a_y, b_x, b_y = q.popleft()
for d in move_ds:
a_dx = a_x + d[0]
a_dy = a_y + d[1]
b_dx = b_x + d[0]
b_dy = b_y + d[1]
if 0 <= a_dx < n and 0 <= a_dy < n and 0 <= b_dx < n and 0 <= b_dy < n:
if (a_dx, a_dy) not in q_set and (b_dx, b_dy) not in q_set:
if check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] == 0:
if check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] == 0:
check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] = check_move_board[a_x][a_y] + 1
# check_move_board[a_x][a_y] = check_move_board[a_x][a_y] + 1
q.append([a_dx, a_dy, a_x, a_y])
for d in cir_ds:
a_dx = a_x + d[0]
a_dy = a_y + d[1]
b_dx = b_x + d[0]
b_dy = b_y + d[1]
if 0 <= a_dx < n and 0 <= a_dy < n and 0 <= b_dx < n and 0 <= b_dy < n:
if (a_dx, a_dy) not in q_set and (b_dx, b_dy) not in q_set:
if check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] == 0:
if check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] == 0:
check_move_board[a_dx][a_dy] = check_move_board[a_x][a_y] + 1
# check_move_board[a_x][a_y] = check_move_board[a_x][a_y] + 1
q.append([a_dx, a_dy, a_x, a_y])
print(*check_move_board, sep='\n')
return check_move_board[n - 1][n - 1] - 1
print(solution([[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 1, 0, 1, 1],[1, 1, 0, 0, 1],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]))
b. 2차 시도 (성공 / 주어진 조건대로 구현하다보니 코드가 난잡한 버전 / 속도는 빠름)
# 최고 속도 버전
# 대신, 코드 중복이 심함
# 이건 bfs가 아니라 구현이야
from collections import deque
def solution(board):
# move_check_board = [i[:] for i in board]
n = len(board)
q = deque()
# 시작 위치, 비용
# (0, 0), (0, 1), 0
q.append((0, 0, 0, 1, 0))
total_pos = set()
total_pos.add((0, 0, 0, 1))
ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
while q:
l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y, cost = q.popleft()
# 이동
for d in ds:
next_l_x = l_x + d[0]
next_l_y = l_y + d[1]
next_r_x = r_x + d[0]
next_r_y = r_y + d[1]
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (next_l_x, next_l_y, next_r_x, next_r_y) not in total_pos:
q.append((next_l_x, next_l_y, next_r_x, next_r_y, cost+1))
total_pos.add((next_l_x, next_l_y, next_r_x, next_r_y))
if (next_l_x == n-1 and next_l_y == n-1) or (next_r_x == n-1 and next_r_y == n-1):
return cost+1
# 회전
for i in [-1, 1]:
# 가로 방향일때
next_l_x = l_x + i
next_l_y = l_y
next_r_x = r_x + i
next_r_y = r_y
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (l_x, l_y, l_x + i, l_y) not in total_pos:
q.append((l_x, l_y, l_x + i, l_y, cost+1))
total_pos.add((l_x, l_y, l_x + i, l_y))
if (next_l_x == n-1 and next_l_y == n-1) or (next_r_x == n-1 and next_r_y == n-1):
return cost+1
if (r_x, r_y, r_x + i, r_y) not in total_pos:
q.append((r_x, r_y, r_x + i, r_y, cost+1))
total_pos.add((r_x, r_y, r_x + i, r_y))
if (next_l_x == n-1 and next_l_y == n-1) or (next_r_x == n-1 and next_r_y == n-1):
return cost+1
# 세로 방향일떄
next_l_x = l_x
next_l_y = l_y + i
next_r_x = r_x
next_r_y = r_y + i
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (l_x, l_y, l_x, l_y + i) not in total_pos:
q.append((l_x, l_y, l_x, l_y + i, cost + 1))
total_pos.add((l_x, l_y, l_x, l_y + i))
if (next_l_x == n-1 and next_l_y == n-1) or (next_r_x == n-1 and next_r_y == n-1):
return cost+1
if (r_x, r_y, r_x, r_y + i) not in total_pos:
q.append((r_x, r_y, r_x, r_y + i, cost + 1))
total_pos.add((r_x, r_y, r_x, r_y + i))
if (next_l_x == n-1 and next_l_y == n-1) or (next_r_x == n-1 and next_r_y == n-1):
return cost+1
# 테스트 1 〉 통과 (0.13ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 2 〉 통과 (0.15ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 3 〉 통과 (0.13ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 4 〉 통과 (0.86ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 5 〉 통과 (0.45ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 6 〉 통과 (0.72ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 7 〉 통과 (1.93ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 8 〉 통과 (2.87ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 9 〉 통과 (2.91ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 10 〉 통과 (2.90ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 11 〉 통과 (1.78ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 12 〉 통과 (2.03ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 13 〉 통과 (60.59ms, 11.8MB)
# 테스트 14 〉 통과 (37.65ms, 11.1MB)
c. 3차 시도 (성공 / 함수화로 코드 중복은 줄였으나, 속도가 조금 느림)
# 코드 중복은 줄였으나, 속도가 조금 느림
from collections import deque
def escape(l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y):
global n
if (l_x == n - 1 and l_y == n - 1) or (r_x == n - 1 and r_y == n - 1):
return True
else:
return False
def put_new_element(q, total_pos, l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y, cost):
q.append((l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y, cost))
total_pos.add((l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y))
return q, total_pos
def solution(board):
# move_check_board = [i[:] for i in board]
global n
n = len(board)
q = deque()
# 시작 위치, 비용
# (0, 0), (0, 1), 0
q.append((0, 0, 0, 1, 0))
total_pos = set()
total_pos.add((0, 0, 0, 1))
ds = ((0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0))
while q:
l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y, cost = q.popleft()
if escape(l_x, l_y, r_x, r_y):
return cost
# 이동
for d in ds:
next_l_x = l_x + d[0]
next_l_y = l_y + d[1]
next_r_x = r_x + d[0]
next_r_y = r_y + d[1]
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (next_l_x, next_l_y, next_r_x, next_r_y) not in total_pos:
q, total_pos = put_new_element(q=q,
total_pos=total_pos,
l_x=next_l_x,
l_y=next_l_y,
r_x=next_r_x,
r_y=next_r_y,
cost=cost+1)
# 회전
for i in [-1, 1]:
# 가로 방향일때
next_l_x = l_x + i
next_l_y = l_y
next_r_x = r_x + i
next_r_y = r_y
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (l_x, l_y, l_x + i, l_y) not in total_pos:
q, total_pos = put_new_element(q=q,
total_pos=total_pos,
l_x=l_x,
l_y=l_y,
r_x=l_x + i,
r_y=l_y,
cost=cost+1)
if (r_x, r_y, r_x + i, r_y) not in total_pos:
q, total_pos = put_new_element(q=q,
total_pos=total_pos,
l_x=r_x,
l_y=r_y,
r_x=r_x + i,
r_y=r_y,
cost=cost+1)
# 세로 방향일떄
next_l_x = l_x
next_l_y = l_y + i
next_r_x = r_x
next_r_y = r_y + i
if 0 <= next_l_x < n and 0 <= next_l_y < n and 0 <= next_r_x < n and 0 <= next_r_y < n:
if board[next_l_x][next_l_y] == 0 and board[next_r_x][next_r_y] == 0:
if (l_x, l_y, l_x, l_y + i) not in total_pos:
q, total_pos = put_new_element(q=q,
total_pos=total_pos,
l_x=l_x,
l_y=l_y,
r_x=l_x,
r_y=l_y + i,
cost=cost+1)
if (r_x, r_y, r_x, r_y + i) not in total_pos:
q, total_pos = put_new_element(q=q,
total_pos=total_pos,
l_x=r_x,
l_y=r_y,
r_x=r_x,
r_y=r_y + i,
cost=cost+1)
# 테스트 1 〉 통과 (0.16ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 2 〉 통과 (0.19ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 3 〉 통과 (0.18ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 4 〉 통과 (0.71ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 5 〉 통과 (0.57ms, 10.5MB)
# 테스트 6 〉 통과 (0.84ms, 10.1MB)
# 테스트 7 〉 통과 (2.30ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 8 〉 통과 (3.31ms, 10.2MB)
# 테스트 9 〉 통과 (3.49ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 10 〉 통과 (3.38ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 11 〉 통과 (1.84ms, 10.3MB)
# 테스트 12 〉 통과 (2.20ms, 10.4MB)
# 테스트 13 〉 통과 (67.55ms, 11.8MB)
# 테스트 14 〉 통과 (42.80ms, 11.4MB)
print(solution([[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 1, 0, 1, 1],[1, 1, 0, 0, 1],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]))
a. 회고
내 풀이
- 첫 시도에 접근은 잘 했지만, 조건들을 분리하지 않고 한번에 처리하려고 했다.
- 로봇이 차지하고 있는 칸 2개를 q에 넣어주는 방식으로 진행했다.
- 로봇이 지나간 자리는 맵에 직접 표시를 해서 다시 접근하지 못하게 했다.
반성
- 다만, 맵에 지나간 자리를 체크하는 방식은 칸 1개만 걸쳐 있어도 접근하지 않는 문제가 발생한다.
- 문제를 완벽히 읽지 못했다. 이동은 없고 회전만 있는 줄 알았는데, 이동도 할 수 있었다..
- 로봇의 이동 조건과 회전 조건을 분리하고 이동 조건과 회전 조건이 가능한 경우를 전부 고려해서 작성하면 한 번에 풀 수 있었을텐데.
C. 문제 해설
이해한 내용을 바탕으로 작성했습니다.
문제에 제시된 조건들을 풀어보면 아래와 같다.
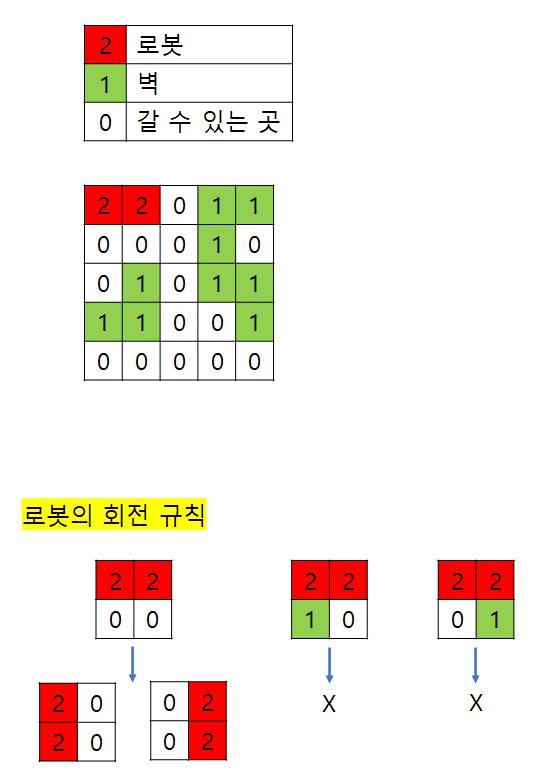
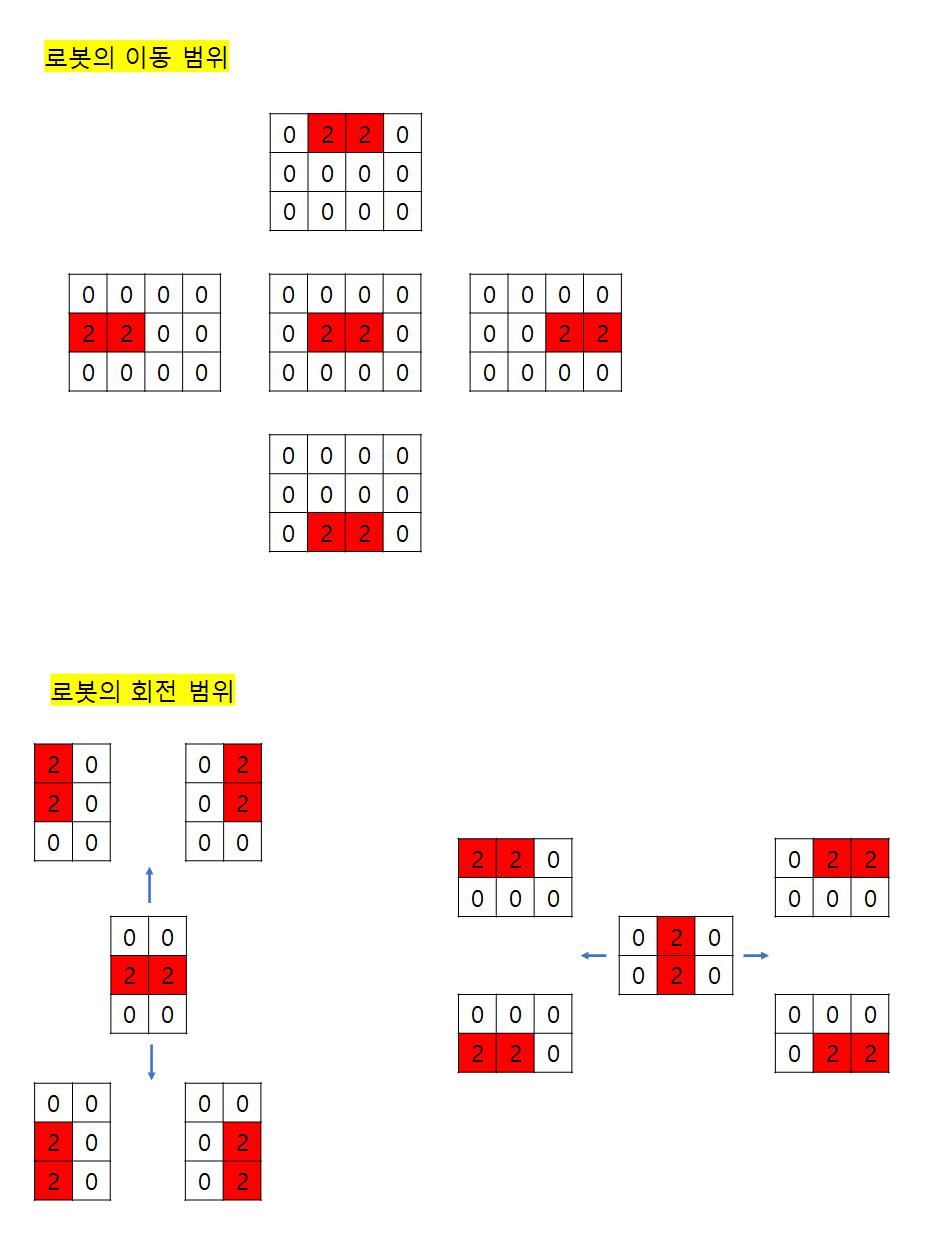
위 조건을 만족하게 코드를 작성하고, 로봇이 방문한 위치도 체크해야 한다. 만약, 로봇이 방문한 위치를 맵에 직접 체크하면 한 칸만 겹치는 경우에도 그 위치에 방문하지 않는다.
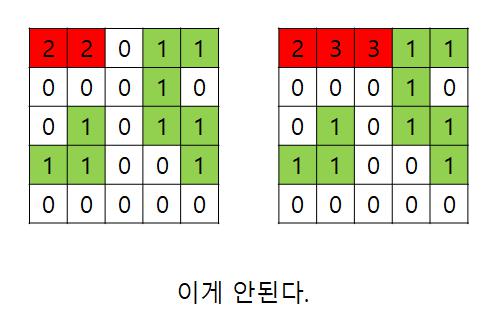
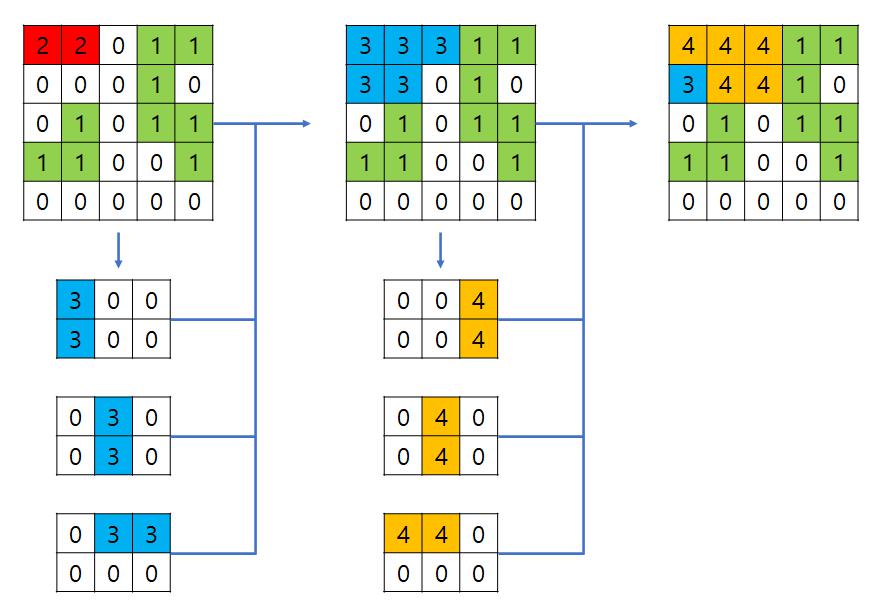
그래서 방문한 위치 2칸을 한번에 저장해야한다. 그리고 2칸이 완전히 겹치는 경우 재방문하지 않는다. 만약 재방문하는 경우 아래와 같이 루프가 발생한다.
솔직히 이 문제는 BFS 문제라기보다는 구현 문제라는 느낌이 들었다.
a. 책 답안
python-for-coding-test/8.py at master · ndb796/python-for-coding-test (github.com)
참고문헌
[1] 나동빈, "이것이 취업을 위한 코딩 테스트다 with 파이썬", 초판, 2쇄, 한빛미디어, 2020년
[2] 코딩테스트 연습 - 블록 이동하기 | 프로그래머스 (programmers.co.kr). Programmers. (accessed Sep 29, 2021)