1. 연산자 끼워 넣기
- 난이도
- 중
- 풀이 시간
- 30분
- 시간 제한
- 2초
- 메모리 제한
- 512 MB
- 출처
A. 문제
위 백준 사이트에 접속하여 문제를 확인해주세요.
B. 내 답안
a. 1차 시도 (성공 / 실행 시간이 오래걸림)
from itertools import permutations
n = int(input())
array = list(map(int, input().split()))
oper = list(map(int, input().split()))
op = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
oper_list = []
for i in range(len(oper)):
for j in range(oper[i]):
oper_list.append(op[i])
# print(oper_list)
combi_oper = list(permutations(oper_list, n-1))
# print(*combi_oper, sep='\n')
max_answer = -1e9
min_answer = 1e9
for i in combi_oper:
answer = array[0]
for j in range(1, n):
if i[j-1] == "+":
answer = answer + array[j]
if i[j-1] == "*":
answer = answer * array[j]
if i[j-1] == "-":
answer = answer - array[j]
if i[j-1] == "/":
if answer < 0:
answer = ((answer * -1) // array[j]) * -1
elif answer > 0:
answer = int(answer // array[j])
else:
pass
# print(i[j-1])
# print(i)
# if max_answer == 0 or min_answer == 1e9:
# max_answer = answer
# min_answer = answer
max_answer = max(answer, max_answer)
min_answer = min(answer, min_answer)
print(max_answer)
print(min_answer)
b. 2차 시도 (성공 / set을 사용하여 실행 시간을 단축함)
from itertools import permutations
n = int(input())
array = list(map(int, input().split()))
oper = list(map(int, input().split()))
op = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
oper_list = []
for i in range(len(oper)):
for j in range(oper[i]):
oper_list.append(op[i])
# print(oper_list)
combi_oper = set(permutations(oper_list, n-1))
# print(*combi_oper, sep='\n')
max_answer = -1e9
min_answer = 1e9
for i in combi_oper:
answer = array[0]
for j in range(1, n):
if i[j-1] == "+":
answer = answer + array[j]
if i[j-1] == "*":
answer = answer * array[j]
if i[j-1] == "-":
answer = answer - array[j]
if i[j-1] == "/":
if answer < 0:
answer = ((answer * -1) // array[j]) * -1
elif answer > 0:
answer = int(answer // array[j])
else:
pass
# print(i[j-1])
# print(i)
# if max_answer == 0 or min_answer == 1e9:
# max_answer = answer
# min_answer = answer
max_answer = max(answer, max_answer)
min_answer = min(answer, min_answer)
print(max_answer)
print(min_answer)
c. 3차 시도 (성공 / 나동빈님의 재귀적 풀이방식을 이해하고 작성)
def recursive(total, oper, i):
global max_answer, min_answer, array, n
# 두 코드(if문)는 같은
# if sum(oper) == 0:
if i == n:
max_answer = max(max_answer, total)
min_answer = min(min_answer, total)
return
else:
if oper[0] != 0:
oper[0] -= 1
recursive(total + array[i], oper, i+1)
oper[0] += 1
if oper[1] != 0:
oper[1] -= 1
recursive(total - array[i], oper, i+1)
oper[1] += 1
if oper[2] != 0:
oper[2] -= 1
recursive(total * array[i], oper, i+1)
oper[2] += 1
if oper[3] != 0:
oper[3] -= 1
recursive(int(total / array[i]), oper, i+1)
oper[3] += 1
global max_answer, min_answer, array, n
n = int(input())
array = list(map(int, input().split()))
oper = list(map(int, input().split()))
max_answer = -1e9
min_answer = 1e9
recursive(array[0], oper, 1)
print(max_answer)
print(min_answer)
d. 4차 시도 (성공 / 어떤 블로그에서 재귀 표현 자체를 직관적으로 이해할 수 있게 풀이한 코드를 이해하고 작성) [3]
def recursive(total, i, add, sub, mul, div):
global max_answer, min_answer, array, n
# 두 코드(if문)는 같은
# if sum(oper) == 0:
if i == n:
max_answer = max(max_answer, total)
min_answer = min(min_answer, total)
return
else:
if add != 0:
recursive(total + array[i], i+1, add-1, sub, mul, div)
if sub != 0:
recursive(total - array[i], i+1, add, sub-1, mul, div)
if mul != 0:
recursive(total * array[i], i+1, add, sub, mul-1, div)
if div != 0:
recursive(int(total / array[i]), i+1, add, sub, mul, div-1)
global max_answer, min_answer, array, n
n = int(input())
array = list(map(int, input().split()))
oper = list(map(int, input().split()))
max_answer = -1e9
min_answer = 1e9
recursive(array[0], 1, oper[0], oper[1], oper[2], oper[3])
print(max_answer)
print(min_answer)
e. 5차 시도 (성공 / 아무리 생각해도 전역변수를 수정하는건 아닌 것 같아서 다시 품)
위 코드들을 보면 함수의 리턴값은 없는데, max와 min 값은 변한다. 전역변수로 처리했기 때문에 그렇다. 그런데 값을 전역변수로 처리하는 행동이 올바른지 잘 모르겠다.
그래서 변하지 않는 값만 전역변수로 사용하는 방식으로 코드를 다시 짯다. 리팩토링이라기에는 복습할겸 백지에서 다시 푼 것이라.. ㅎㅎ
def recursive(result, depth, add, sub, mul, div, max_answer, min_answer):
global N, array
if depth == N:
max_answer = max(result, max_answer)
min_answer = min(result, min_answer)
elif depth != N:
if add > 0:
max_answer, min_answer = recursive(result + array[depth], depth+1, add-1, sub, mul, div, max_answer, min_answer)
if sub > 0:
max_answer, min_answer = recursive(result - array[depth], depth+1, add, sub-1, mul, div, max_answer, min_answer)
if mul > 0:
max_answer, min_answer = recursive(result * array[depth], depth+1, add, sub, mul-1, div, max_answer, min_answer)
if div > 0:
max_answer, min_answer = recursive(int(result / array[depth]), depth+1, add, sub, mul, div-1, max_answer, min_answer)
return max_answer, min_answer
global N, array
N = int(input())
array = list(map(int, input().split()))
oper = list(map(int, input().split()))
max_answer = -1e9
min_answer = 1e9
max_answer, min_answer = recursive(array[0], 1, oper[0], oper[1], oper[2], oper[3], max_answer, min_answer)
print(max_answer)
print(min_answer)
f. 회고
내 풀이
- combination은 아닌 것 같고 permutation인 것 같아서 permutation을 사용했다.
- 연산자 3개 중에 3개를 뽑는데 순서가 있는 경우에서 최댓값과 최솟값을 뽑는 경우이기 때문에 permutation이라 판단했다.
- 백준 채점에 1분 20초가 넘게 걸린 듯 하다.
반성
- 속도 개선을 위해 불필요하게 연산을 반복하는 부분을 제거할 필요가 있다.
결론
- 다양한 풀이가 있고, 내 풀이가 완벽하지 않다는 것을 알았다. 특히 extend 함수가 있다는 것을 처음 알았다.
C. 문제 해설
이해한 내용을 바탕으로 작성했습니다.
연산 순서마다 값이 다 다르게 변한다. 따라서 모든 경우를 계산할 필요가 있다.
단순히 permutation을 사용하면 연산이 중복되는 지점을 새로 연산해야하기 때문에 시간이 오래걸린다.
그래서 재귀로 풀면 아래 그림과 같이 동작한다.
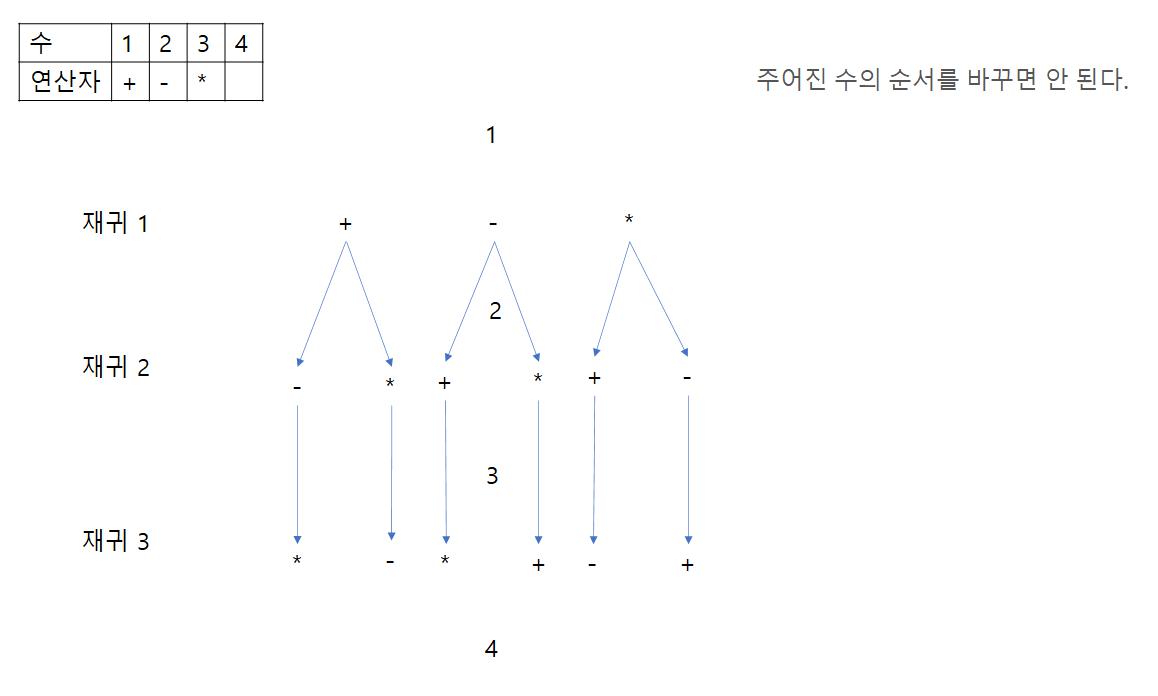
나누기(/)연산을 //가 아닌 int(A/B)를 하는 이유는 아래 코드에서 확인할 수 있다.
-1/3
-0.3333333333333333
int(-1/3)
0
-1//3
-1
a. 책 답안
python-for-coding-test/5.py at master · ndb796/python-for-coding-test (github.com)
참고문헌
[1] 나동빈, "이것이 취업을 위한 코딩 테스트다 with 파이썬", 초판, 2쇄, 한빛미디어, 2020년
[2] 14888번: 연산자 끼워넣기 (acmicpc.net). Baekjoon. (accessed Sep 24, 2021)
[3] 개발하는 다임하게. Daim's blog :: Python으로 푸는 백준 14888. 연산자 끼워넣기 (tistory.com). tistory. (accessed Sep 24, 2021)