1. 연구소
- 난이도
- 중
- 풀이 시간
- 40분
- 시간 제한
- 2초
- 메모리 제한
- 512 MB
- 출처
A. 문제
위 백준 사이트에 접속하여 문제를 확인해주세요.
B. 내 답안
a. 1차 시도 (실패)
def dfs(graph, x, y):
d = ((-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1))
if x < 0 or x >= n or y < 0 or y >= m:
return None
if graph[x][y] == 1:
return None
if graph[x][y] == 0:
graph[x][y] = 2
dfs(graph, x - 1, y)
dfs(graph, x + 1, y)
dfs(graph, x, y + 1)
dfs(graph, x, y - 1)
# if graph[x][y] != 2:
# dfs(graph, x - 1, y)
# dfs(graph, x + 1, y)
# dfs(graph, x, y - 1)
# dfs(graph, x, y + 1)
return True
global n
global m ###
# 세로, 가로
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 0 빈칸 / 1 벽 / 2 바이러스
graph = []
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
graph_check = [i[:] for i in graph]
answer = 0
end_count = (m*n)
while end_count > 0:
wall_count = 3
graph_temp = [i[:] for i in graph]
safe_count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph_temp[i][j] == 0 and graph_check[i][j] == 0:
graph_temp[i][j] = 1
wall_count -= 1
if wall_count == 0:
break
graph_check[i][j-2] = 1
if wall_count == 0:
break
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph_temp[i][j] == 2:
graph_temp[i][j] = 0
dfs(graph_temp, i, j)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph_temp[i][j] == 0:
safe_count += 1
answer = max(answer, safe_count)
end_count -= 1
print(*graph_temp, sep='\n')
print()
print(*graph_check, sep='\n')
print()
print(answer)
b. 2차 시도 (성공)
def check_virus(graph, x, y):
global n, m
ds = ((1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1))
for d in ds:
dx = x + d[0]
dy = y + d[1]
if dx < 0 or dx >= n or dy < 0 or dy >= m:
continue
if graph[dx][dy] == 1:
continue
if graph[dx][dy] != 2:
graph[dx][dy] = 2
check_virus(graph, dx, dy)
def dfs(count, graph):
global answer
if count == 3:
# 벽 3개 다 침
temp_graph = [i[:] for i in graph]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 2:
check_virus(temp_graph, i, j)
safe_count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if temp_graph[i][j] == 0:
safe_count += 1
answer = max(answer, safe_count)
# return answer
else:
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 0:
count += 1
graph[i][j] = 1
dfs(count, graph)
graph[i][j] = 0
count -= 1
global n, m
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = []
global answer
answer = 0
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
dfs(0, graph)
print(answer)
c. 3차 시도 (combination 사용)
from itertools import combinations
def dfs(graph, x, y):
global n, m
ds = ((1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1))
for d in ds:
dx = x + d[0]
dy = y + d[1]
if 0 <= dx < n and 0 <= dy < m:
if graph[dx][dy] == 0:
graph[dx][dy] = 2
dfs(graph, dx, dy)
else:
continue
else:
continue
global n, m
n, m = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = []
empty = []
virus = []
for i in range(n):
temp = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph.append(temp)
for j in range(len(temp)):
if temp[j] == 0:
empty.append((i, j))
elif temp[j] == 2:
virus.append((i, j))
empty_combinations = list(combinations(empty, 3))
answer = 0
for emptys in empty_combinations:
# 벽 세우기
for empty in emptys:
x, y = empty
graph[x][y] = 1
# 바이러스 확산
temp_graph = [i[:] for i in graph]
for v in virus:
vx, vy = v
dfs(temp_graph, vx, vy)
count = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if temp_graph[i][j] == 0:
count += 1
answer = max(count, answer)
# print(*temp_graph, sep='\n')
# print()
# 벽 내리기
for empty in emptys:
x, y = empty
graph[x][y] = 0
print(answer)
d. 회고
내 풀이
- dfs 알고리즘으로 해결할 수 있겠다는 생각은 들었으나, 어떤 방식을 사용해야지 벽 3개를 모든 구간에 올릴 수 있을지 생각하지 못했다.
C. 문제 해설
이해한 내용을 바탕으로 작성했습니다.
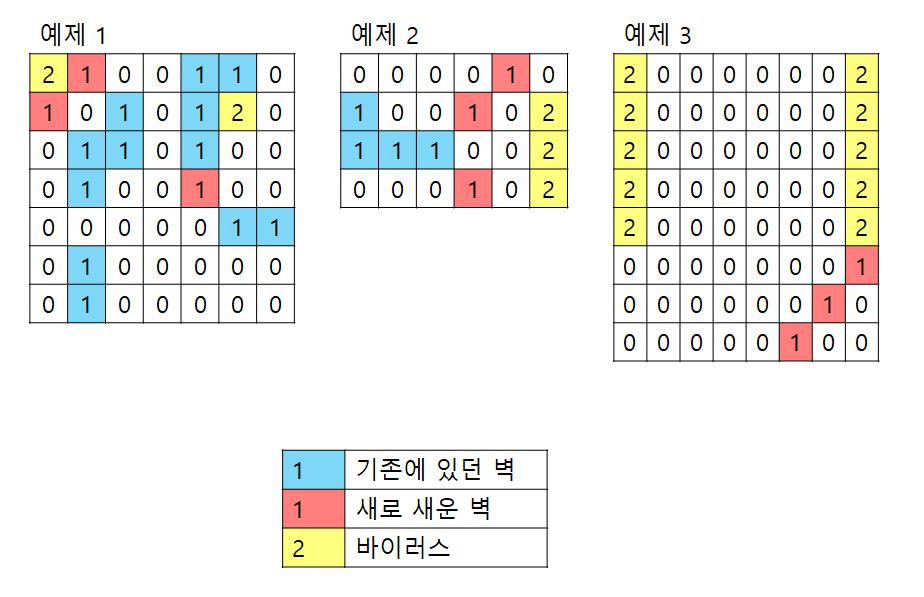
- 벽 3개를 세운다
- 바이러스를 dfs로 퍼트린다.
- 바이러스가 감염되지 않은 0의 개수를 구한다.
- 0의 개수가 최대가 될 때까지 위 과정을 반복한다.
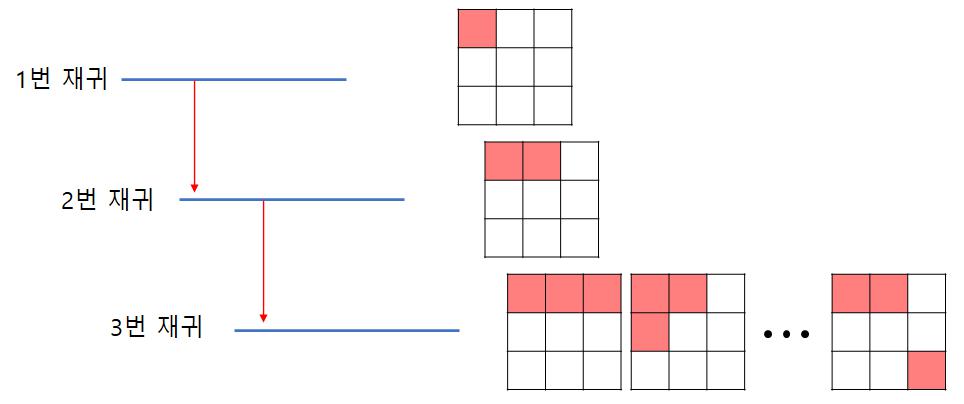
벽을 모든 구간에 세우기 위해 재귀 함수를 3번 호출한다. 한개의 재귀함수는 벽 한개를 세운다. 이 방법은 완전탐색으로 매우 비효율적이지만, 지도의 크기가 최대 8*8이기 때문에 사용할 수 있다. (최악의 경우 ${64}C{3}$)
바이러스 감염은 간단하게 dfs로 채우면 된다.
a. 책 답안
python-for-coding-test/2.py at master · ndb796/python-for-coding-test (github.com)
참고문헌
[1] 나동빈, "이것이 취업을 위한 코딩 테스트다 with 파이썬", 초판, 2쇄, 한빛미디어, 2020년
[2] 14502번: 연구소 (acmicpc.net). Baekjoon. (accessed Sep 23, 2021)