REPL 사용하기
- READ(읽기) / EVAL(해석) / PRINT(반환) / LOOP(반복)
- 정보를 읽어 해석한 것을 출력하는 과정을 반복하는 것을 의미
- 미리 컴파일하지 않아도 콘솔을 통해 사용 가능함
JS 파일 실행하기
function helloWorld() {
console.log('Hello World');
helloNode();
}
function helloNode() {
console.log('Hello Node');
}
helloWorld();
$ node helloWorld
Hello World
Hello Node
모듈 만들기
- 모듈 : 특정한 기능을 하는 함수나 변수들의 집합
- 모듈을 만들어두면 필요한 기능의 코드를 재사용할 수 있음
- ES2015 모듈 : 자체 모듈 시스템 문법
- require -> import / module.exports -> export default
- 파일 확장자를 mjs로 바꾸거나 package.json에 type: "module" 속성을 넣어야함
- var.js
const odd = '홀수';
const even = '짝수';
// 파일 불러오면 export default(module.exports)에 대입된 값 사용
export default {
odd,
even,
};
- func.js
// const { odd, even } = require('./var');
import { odd, even } from './var.mjs';
function checkOddOrEven(num) {
if(num % 2) {
return odd;
}
return even;
}
export default checkOddOrEven;
- index.js
import { odd, even } from './var.mjs';
import checkNumber from './func.mjs';
function checkStringOddOrEven(str) {
if (str.length % 2) {
return odd;
}
return even;
}
console.log(checkNumber(10));
console.log(checkStringOddOrEven('Hello'));
노드 내장 객체 알아보기
global
- 브라우저의 window와 같은 전역 객체
- 모든 파일에서 접근 가능
- window.open(window.console)을 open(console)으로 호출하는 것 처럼 global도 생략 가능
$ node
> global
{
global: [Circular *1],
clearInterval: [Function: clearInterval]
clearTimeout: [Function: clearTimeout]
...
}
> global.console
{
log: [Function: bound consoleCall],
warn: [Function: bound consoleCall],
dir: [Function: bound consoleCall],
...
}
import A from './globalA.mjs';
global.message = '안녕하세요';
console.log(A());
export default () => global.message;
$ node globalB
안녕하세요
console
- 디버깅을 위해 사용
- console.time(레이블) / console.timeEnd(레이블) : 서로 대응되며, 같은 레이블을 가진 time과 timeEnd 사이 시간 측정
- console.log(내용) : 로그들을 콘솔에 표시
- console.error(에러 내용) : 에러를 콘솔에 표시
- console.table(배열) : 배열 요소로 객체 리터럴을 넣으면 객체 속성들이 테이블 형식으로 표현
- console.dir(객체, 옵션) : 객체를 콘솔에 표시할 떄 사용
- 첫 번째 인수 : 표시할 객체
- 두 번째 인수 : 옵션
- colors : 경우 true로 할 경우 콘솔에 색이 추가
- depth : 객체 안의 객체를 몇 단계까지 보여줄 지 결정(기본값 : 2)
- console.trace(레이블) : 에러가 어디서 발생했는지 추적
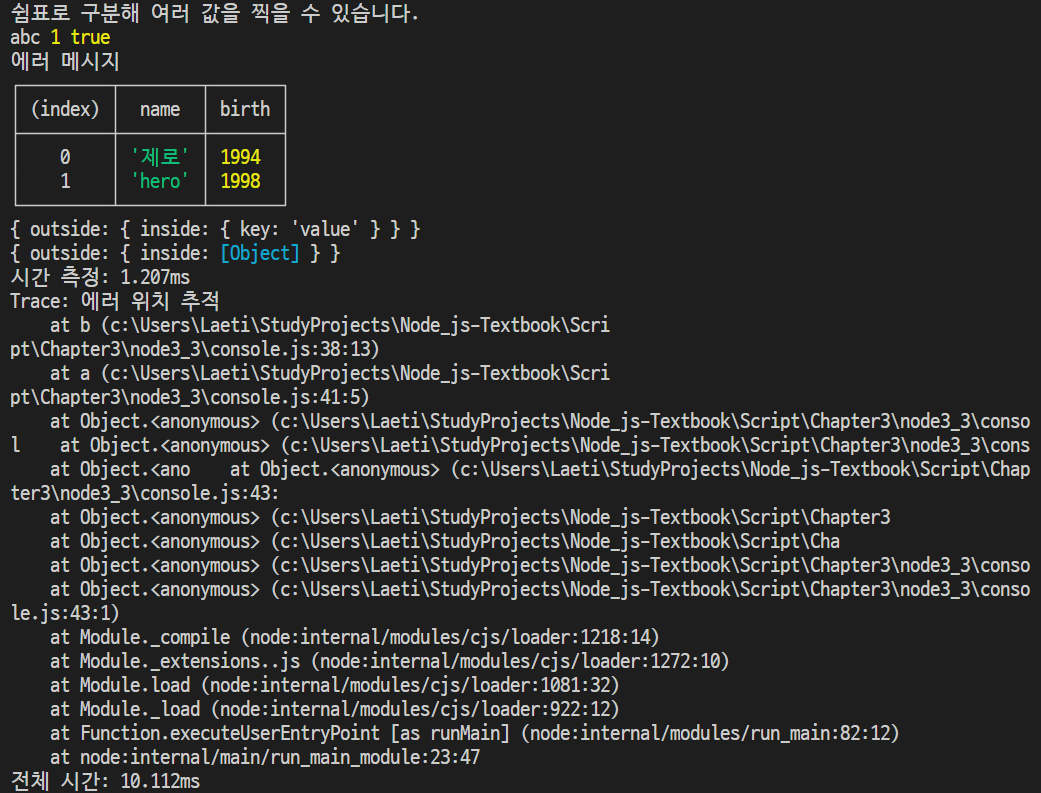
const string = 'abc';
const number = 1;
const boolean = true;
const obj = {
outside: {
inside: {
key: 'value'
},
},
};
console.time('전체 시간');
console.log('쉼표로 구분해 여러 값을 찍을 수 있습니다.');
console.log(string, number, boolean);
console.error('에러 메시지');
console.table([{
name: '제로',
birth: 1994
}, {
name: 'hero',
birth: 1998
}]);
console.dir(obj, {
colors: false,
depth: 2,
});
console.dir(obj, {
colors: true,
depth: 1,
});
console.time('시간 측정');
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { }
console.timeEnd('시간 측정');
function b() {
console.trace('에러 위치 추적');
}
function a() {
b();
}
a();
console.timeEnd('전체 시간');
타이머
- setTimeout(콜백 함수, 밀리초) : 주어진 밀리초 이후에 콜백 함수 실행
- setInterval(콜백 함수, 밀리초) : 주어진 밀리초마다 콜백 함수 반복 실행
- setImmediate(콜백 함수) : 콜백 함수 즉시 실행
- clearTimeout(아이디) : setTimeout을 취소
- clearInterval(아이디) : setInterval을 취소
- clearImmediate(아이디) : setImmediate를 취소
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('1.5초 후 실행');
}, 1500);
const interval = setInterval(() => {
console.log('1초마다 실행');
}, 1000);
const timeout2 = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('실행되지 않습니다.');
}, 3000);
setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timeout2);
clearInterval(interval);
}, 2500);
const immediate = setImmediate(() => {
console.log('즉시 실행');
});
const immediate2 = setImmediate(() => {
console.log('실행되지 않습니다.');
});
clearImmediate(immediate2);
즉시 실행
1초마다 실행
1.5초 후 실행
1초마다 실행
__filename, __dirname
- 현재 파일명과 파일 경로에 대한 정보 확인 가능
console.log(__filename);
console.log(__dirname);
c:\Users\Laeti\StudyProjects\Node_js-Textbook\Script\Chapter3\node3_4\filename.js
c:\Users\Laeti\StudyProjects\Node_js-Textbook\Script\Chapter3\node3_4
module, exports, require
- 모듈을 만드는 객체
- this 특징
- 최상위 스코프에 존재하는 this는 module.exports를 가리킴
- 함수 선언문 내부 this는 global 객체를 가리킴
console.log(this); console.log(this === module.exports); console.log(this === exports); function whatIsThis() { console.log('function', this === exports, this === global); } whatIsThis();{} true true function false true
- require
- cache
- 파일에 대한 속성이나 모듈 관계 등 cache 정보 확인
- 한 번 require한 파일은 require.cache에 저장
- 새로 require할 경우 require.cache의 속성을 제거해야 함
- main : 노드 실행 시 첫 모듈을 가리킴
console.log("require가 가장 위에 올 필요가 없습니다."); module.expports = "저를 찾아보세요."; require('./var'); console.log('require.cache입니다.'); console.log(require.cache); // 파일명에 대한 정보 출력 console.log('require.main입니다.'); console.log(require.main === module); // 현재 파일이 첫 모듈인지 확인 console.log(require.main.filename); // 첫 모듈 파일명 확인
- cache
- 순환 참조가 있을 경우 대상을 빈 객체로 표시
- dep1.js
const dep2 = require('./dep2'); console.log('require dep2', dep2); module.exports = () => { console.log('dep2', dep2); };- dep2.js
dep-run.jsconst dep1 = require('./dep1'); console.log('require dep1', dep1); module.exports = () => { console.log('dep1', dep1); };const dep1 = require('./dep1'); const dep2 = require('./dep2'); dep1(); dep2();
require dep1 {}
require dep2 [Function (anonymous)]
dep2 [Function (anonymous)]
dep1 {}
process
현재 실행되고 있는 노드 프로세스에 대한 정보를 담고 있음
process.version : 설치된 노드 버전 확인
process.arch : 프로세서 아키텍처 정보 (arm, ia32 등의 값)
process.platform : 운영체제 플랫폼, linux나 darwin, freebsd 등의 값
process.pid : 현재 프로세스 아이디, 프로세스 여러 개를 가질 때 구분할 수 있음
process.uptime() : 프로세스가 시작된 후 흐른 시간, 초단위로 진행
process.exePath : 노드의 경로
process.cwd() : 현재 프로세스가 실행되는 위치
process.cpuUsage : 현재 cpu 사용량
process.env : 시스템 환경 변수
process.nextTick(콜백) : 이벤트 루프가 다른 콜백 함수들보다 nextTick의 콜백 함수를 우선으로 처리하도록 만듦
- process.nextTick와 Promise를 마이크로태스크(microtask)라 부름
- 이벤트 루프는 마이크로태스크를 우선하기 때문에 재귀 호출은 다른 콜백 함수들이 실행되지 않을 수 있음
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('immediate');
});
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('nextTick');
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout');
}, 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('promise'));
$ node nextTick
nextTick
promise
timeout
immediate
process.exit(노드 프로세스)
- 실행중인 노드 프로세스 종료
let i = 1;
setInterval(() => {
if (i === 5) { // i가 5가 되었을 때 종료
console.log('종료!');
process.exit();
}
console.log(i);
i += 1;
}, 1000);
노드 내장 모듈
os
- 사용자 컴퓨터의 운영체제 정보를 가져옴
- os.arch() : process.arch와 동일, 프로세서 아키텍처 정보 (arm, ia32 등의 값)
- os.platform() : process.platform과 동일, 운영체제 플랫폼, linux나 darwin, freebsd 등의 값
- os.type() : 운영체제의 종류
- os.uptime() : 운영체제 부팅 이후 흐른 시간(초), 노드의 실행 시간
- os.hostname() : 컴퓨터의 이름
- os.release() : 운영체제 버전
- 경로
- os.homedir() : 홈 디렉터리 경로
- os.tmpdir() : 임시 파일 저장 경로
- CPU 정보
- os.cpus() : 컴퓨터의 코어 정보
- os.freemem() : 사용 가능한 메모리(RAM)
- os.totalmem() : 전체 메모리 용량
path
- 폴더와 파일의 경로를 쉽게 조작하도록 도와주는 모듈
- path.sep : 경로의 구분자, 윈도 : \로 경로 구분, POSIX : /로 경로 구분
- path.delimiter : 환경 변수의 구분자
- path.dirname(경로) : 파일이 위치한 폴더 경로
- path.extname(경로) : 파일의 확장자
- path.basename(경로, 확장자) : 파일의 이름과 확장자를 표시, 확장자 인수값을 넣을 시 파일 이름만 표시
- path.parse(경로) : 파일 경로를 root, dir, base, ext, name으로 분리
- path.format(객체) : path.parse()한 객체를 파일 경로로 합침
- path.normalize(경로) : /나 \를 실수로 여러번 사용하거나 혼용한 경우 정상적인 경로롤 변환
- path.isAbsolute(경로) : 파일의 경로가 절대경로인지 상대경로인지를 true나 false로 알림
- path.relative(기준경로, 비교경로) : 경로를 두 개 넣으면 첫 번째 경로에서 두 번째 경로로 가는 방법을 알려줌
- path.join(경로, ...) : 여러 인수를 넣으면 하나의 경로로 합침 상대경로인 ..(부모 디렉터리)과 .(현 위치)도 알아서 처리
- path.resolve(경로, ...) : path.join()과 다르게 절대경로로 인식하여 앞의 경로 무시
- path.join('/a', '/b'. '/c'); /* 결과 : /a/b/c/ */
- path.resolve('/a', '/b', 'c'); /* 결과 : /b/c */
url
- 인터넷 주소를 쉽게 조작하도록 도와주는 모듈
- 노드 버전 7에서 추가된 WHATWG(웹 표준 단체) 방식 url과 예전 노드에서 사용한 방식 url이 존재
- url.parse(주소) : 주소를 분해, WHATWG 방식과 비교하면 username과 password 대신 auth 속성이 있고, searchParams 대신 query가 있음
- url.format(객체) : WHATWG 방식 url과 기존 노드의 url을 모두 사용할 수 있음
const url = require('url'); // WHATWG 방식 url
// 기존 방식 url
const { URL } = url;
const myURL = new URL('http://www.gilbut.co.kr/book/bookList.aspx?sercate1=001001000#anchor');
console.log('new URL():', myURL);
console.log('url.format():', url.format(myURL));
new URL(): URL {
href: 'http://www.gilbut.co.kr/book/bookList.aspx?sercate1=001001000#anchor',
origin: 'http://www.gilbut.co.kr',
protocol: 'http:',
username: '',
password: '',
host: 'www.gilbut.co.kr',
hostname: 'www.gilbut.co.kr',
port: '',
pathname: '/book/bookList.aspx',
search: '?sercate1=001001000',
searchParams: URLSearchParams { 'sercate1' => '001001000' },
hash: '#anchor'
}
url.format(): http://www.gilbut.co.kr/book/bookList.aspx?sercate1=001001000#anchor
- searchParams 객체 : WHATWG 방식에서 반환되는 객체
- search는 주소를 통해 데이터 전달할 때 사용, 물음표(?)로 시작해 그 뒤에 키=값 형식으로 데이터 전달, 여러 키인 경우 &로 구분
const myURL = new URL('http://www.gilbut.co.kr/?page=3&limit=10&category=nodejs&category=javascript');
console.log('searchParams:', myURL.searchParams);
console.log('searchParams.getAll():', myURL.searchParams.getAll('category'));
console.log('searchParams.get():', myURL.searchParams.get('limit'));
console.log('searchParams.has():', myURL.searchParams.has('page'));
console.log('searchParams.keys():', myURL.searchParams.keys());
console.log('searchParams.values():', myURL.searchParams.values());
myURL.searchParams.append('filter', 'es3');
myURL.searchParams.append('filter', 'es5');
console.log(myURL.searchParams.getAll('filter'));
myURL.searchParams.set('filter', 'es6');
console.log(myURL.searchParams.getAll('filter'));
myURL.searchParams.delete('filter');
console.log(myURL.searchParams.getAll('filter'));
console.log('searchParams.toString():', myURL.searchParams.toString());
myURL.search = myURL.searchParams.toString();
searchParams: URLSearchParams {
'page' => '3',
'limit' => '10',
'category' => 'nodejs',
'category' => 'javascript' }
searchParams.getAll(): [ 'nodejs', 'javascript' ]
searchParams.get(): 10
searchParams.has(): true
searchParams.keys(): URLSearchParams Iterator { 'page', 'limit', 'category', 'category' }
searchParams.values(): URLSearchParams Iterator { '3', '10', 'nodejs', 'javascript' }
[ 'es3', 'es5' ]
[ 'es6' ]
[]
searchParams.toString(): page=3&limit=10&category=nodejs&category=javascript
객체 조작 메서드
- getAll(키) : 키에 해당하는 모든 값들을 가져옴
- get(키) : 키에 해당하는 첫 번째 값만 가져옴
- has(키) : 해당 키가 있는지 없는지 검사
- keys() : searchParams의 모든 키를 반복기(iterator) 객체로 가져옴
- values() : searchParams의 모든 값을 반복기 객체로 가져옴
- append(키, 값) : 키를 추가, 같은 값의 키가 있으면 유지하고 하나 더 추가
- set(키, 값) : 같은 값 키를 모두 지우고 새로 추가
- delete(키) : 해당 키 제거
- toString() : 조작한 searchParams 객체를 다시 문자열로 만듦, search에 대입하면 주소 객체에 반영
querystring
- 기존 방식 url을 사용할 때, search부분을 사용하기 쉽게 객체로 만드는 모듈
- querystring.parse(쿼리) : url query 부분을 자바스크립트 객체로 분해
- querystring.stringify(객체) : 분해된 query 객체를 문자열로 다시 조립
const url = require('url');
const querystring = require('querystring');
const parsedUrl = url.parse("http://www.gilbut.co.kr/?page=3&limit=10&category=nodejs&category=javascript");
const query = querystring.parse(parsedUrl.query);
console.log('querystring.parse() : ', query);
console.log('querystring.stringify() : ', querystring.stringify(query));
querystring.parse() : [Object: null prototype] {
page: '3',
limit: '10',
category: [ 'nodejs', 'javascript' ]
}
querystring.stringify() : page=3&limit=10&category=nodejs&category=javascript
crypto
다양한 방식의 암호화를 도와주는 모듈
단방향 암호화 : 비밀번호에 사용하는 암호화, 복호화할 수 없는 암호화 방식을 의미. 해시 기법을 주로 사용
- 해시 기법 : 어떠한 문자열을 고정된 길이의 다른 문자열로 바꿔버리는 방식

- createHash(알고리즘) : 사용할 해시 알고리즘을 넣음, md5와 sha1은 이미 취약점이 발견
- update(문자열) : 변환할 문자열을 넣음
- digest(인코딩) : 인코딩할 알고리즘을 넣음, base64, hex, latin1 등이 있음
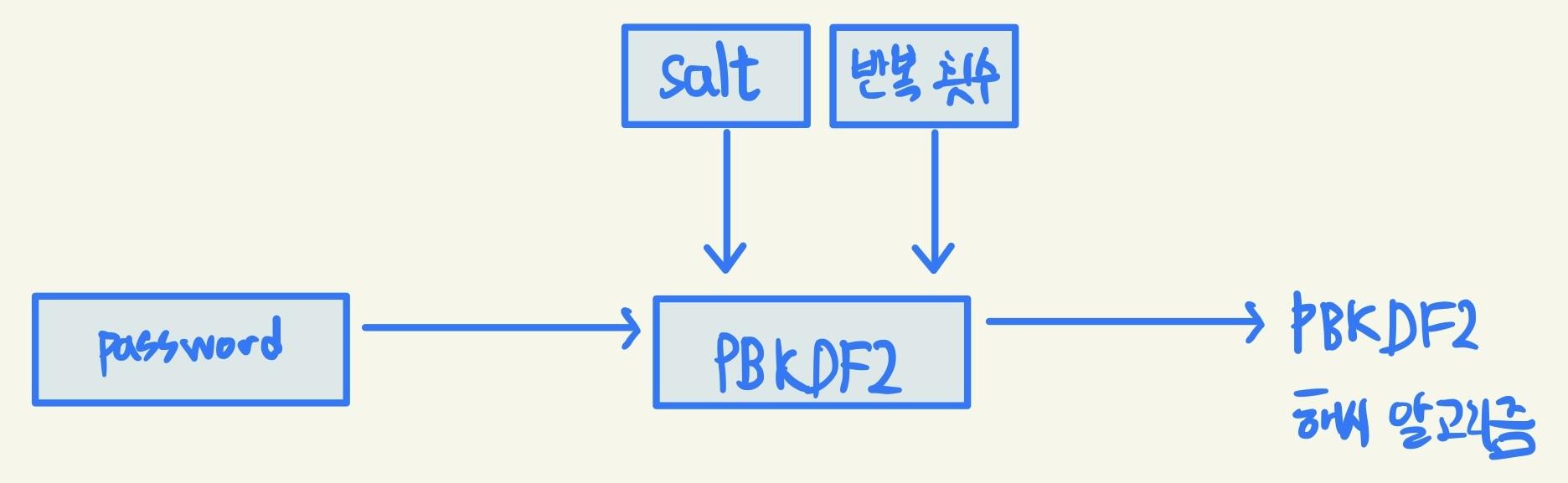
const crypto = require('crypto'); console.log('base64:', crypto.createHash('sha512').update('비밀번호').digest('base64')); console.log('hex:', crypto.createHash('sha512').update('비밀번호').digest('hex')); console.log('base64:', crypto.createHash('sha512').update('다른 비밀번호').digest('base64'));base64: dvfV6nyLRRt3NxKSlTHOkkEGgqW2HRtfu19Ou/psUXvwlebbXCboxIPmDYOFRIpqav2eUTBFuHaZri5x+usy1g== hex: 76f7d5ea7c8b451b773712929531ce92410682a5b61d1b5fbb5f4ebbfa6c517bf095e6db5c26e8c483e60d8385448a6a6afd9e513045b87699ae2e71faeb32d6 base64: cx49cjC8ctKtMzwJGBY853itZeb6qxzXGvuUJkbWTGn5VXAFbAwXGEOxU2Qksoj+aM2GWPhc1O7mmkyohXMsQw==- pbkdf2 : 기존 문자열에 salt라고 불리는 문자열을 붙인 후 해시 알고리즘을 반복해서 적용

const crypto = require('crypto'); crypto.randomBytes(64, (err, buf) => { const salt = buf.toString('base64'); console.log('salt:', salt); crypto.pbkdf2('비밀번호', salt, 100000, 64, 'sha512', (err, key) => { // 알고리즘 10만회 반복해서 적용 console.log('password:', key.toString('base64')); }); });salt: nt/WvMfQuxy87m3G6yGZvuyamTvmhmx54ME5ns7YZq38Gq1UHkULcOKpmzyiL+49wAOuVZXQIN2THidlJl3U3w== password: PAtnwM8inzx5PxmOCDv78bYnQEx9K4dd9O8AbL9AYViTYfBG6J5EjeOaNsAdr/6YTEwjtD93n2p9jIuW9b0kew==- 해시 기법 : 어떠한 문자열을 고정된 길이의 다른 문자열로 바꿔버리는 방식
양방향 암호화 : 키를 통해 암호화된 문자열을 복호화할 수 있음
const crypto = require('crypto');
const algorithm = 'aes-256-cbc';
const key = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz123456';
const iv = '1234567890123456';
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(algorithm, key, iv);
let result = cipher.update('암호화할 문장', 'utf8', 'base64');
result += cipher.final('base64');
console.log('암호화:', result);
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv(algorithm, key, iv);
let result2 = decipher.update(result, 'base64', 'utf8');
result2 += decipher.final('utf8');
console.log('복호화:', result2);
암호화: iiopeG2GsYlk6ccoBoFvEH2EBDMWv1kK9bNuDjYxiN0=
복호화: 암호화할 문장
util
- 각종 편의 기능을 모아둔 모듈
- util.deprecate : deprecate 처리된 함수임을 알림
- util.promisify : 콜백 패턴을 프로미스 패턴으로 바꿈
const util = require('util');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const dontUseMe = util.deprecate((x, y) => {
console.log(x + y);
}, 'dontUseMe 함수는 deprecated되었으니 더 이상 사용하지 마세요!');
dontUseMe(1, 2);
const randomBytesPromise = util.promisify(crypto.randomBytes);
randomBytesPromise(64)
.then((buf) => {
console.log(buf.toString('base64'));
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});
3
(node:96184) DeprecationWarning: dontUseMe 함수는 deprecated되었으니 더 이상 사용하지 마세요!
(Use `node --trace-deprecation ...` to show where the warning was created)
aBVbBkVkNuz/uHCxXp3H2j5k6mLpVN1HktwUK3WYykU48ZfiOaA7/r+OyJuoUxU21VosJRDzRz/iLciq1SAg3w==
worker_threads : 노드에서 멀티 스레드 방식으로 작업
const {
Worker, isMainThread, parentPort,
} = require('worker_threads');
// 메인 스레드에서 실행되는지 생성한 워커 스레드에 실행되는지 구분
if (isMainThread) { // 부모일 때
const worker = new Worker(__filename);
worker.on('message', message => console.log('from worker', message));
worker.on('exit', () => console.log('worker exit'));
worker.postMessage('ping');
} else { // 워커일 때
parentPort.on('message', (value) => {
console.log('from parent', value);
parentPort.postMessage('pong');
parentPort.close();
});
}
from parent ping
from worker pong
worker exit
child_process
- 노드에서 다른 프로그램을 실행하고 싶거나 명령어를 수행하고 싶을 때 사용하는 모듈
- 다른 언어 코드를 실행하고 결과값을 받을 수 있음
- 현재 노드 프로세스 외 새로운 프로세스를 띄워 명령을 수행하고 노드 프로세스에 결과를 알려줄 수 있음
const exec = require('child_process').exec;
const process = exec('dir');
process.stdout.on('data', function(data) {
console.log(data.toString());
}); // 실행 결과
process.stderr.on('data', function(data) {
console.error(data.toString());
}); // 실행 에러
2022-12-15 ���� 03:55 <DIR> .
2022-12-14 ���� 08:32 <DIR> ..
2022-12-29 ���� 11:20 <DIR> Image
2022-12-29 ���� 11:20 <DIR> Markdown
2022-12-15 ���� 01:49 <DIR> Script
0�� ���� 0 ����Ʈ
5�� ���� 250,540,572,672 ����Ʈ ����
기타 모듈
- assert : 값을 비교하여 프로그램이 제대로 동작하는지 테스트
- dns : 도메인 이름에 대한 IP 주소를 얻어냄
- net : HTTP보다 로우 레벨인 TCP나 IPC 통신을 할 때 사용
- string_decoder : 버퍼 데이터를 문자열로 바꾸는 데 사용
- tls : TLS와 SSL에 관련한 작업을 할 때 사용
- tty : 터미널과 관련된 작업을 할 때 사용
- dgram : UDP와 관련된 작업을 할 때 사용
- v8 : V8 엔진에 직접 접근할 때 사용
- vm : 가상 머신에 직접 접근할 때 사용
참고 문헌
조현영, 『Node.js 교과서』, 개정 2판, 길벗출판사, 2020